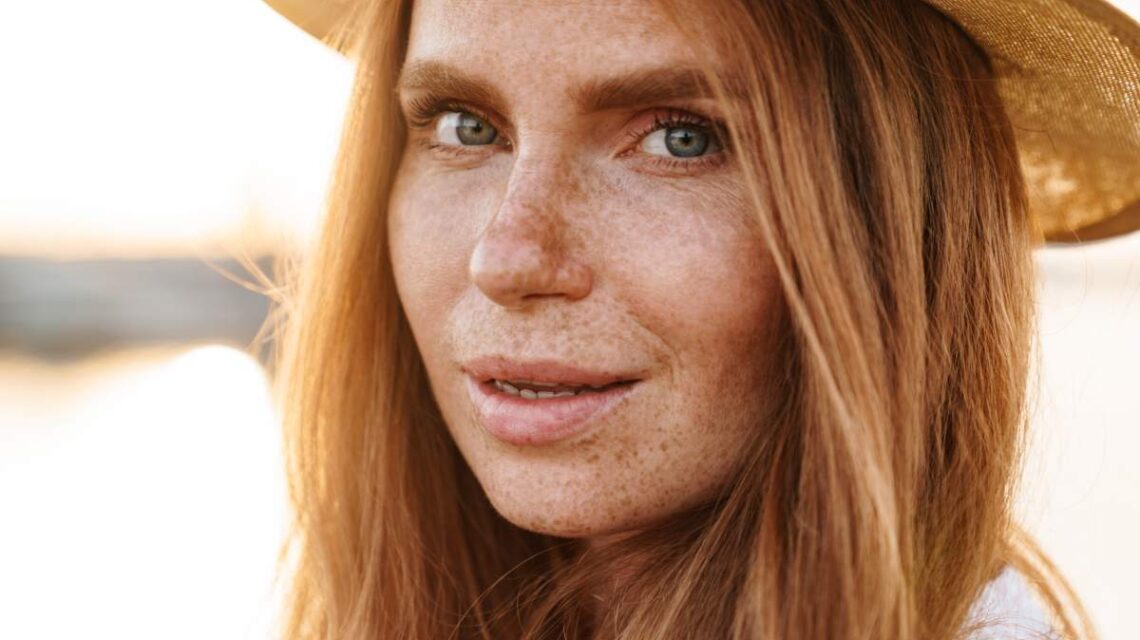
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that affects millions worldwide. Among the most prevalent types are melasma, freckles, and age spots, which can cause uneven skin tone, blotchy patches, and an overall appearance of ageing. While these skin conditions are not harmful, they can be distressing for those who experience them, prompting questions about removal options.
This article will delve into what melasma, freckles, and age spots are and why they occur, as well as explore various methods for their treatment and removal.
More to read:
Understanding Melasma, Freckles, and Age Spots
Before discussing treatment options, it’s important to understand what distinguishes these conditions.
Melasma
Melasma is a skin condition characterized by dark, irregular patches, often found on the face. It most commonly affects women, especially during pregnancy, due to hormonal changes. Melasma is also referred to as “the mask of pregnancy.” The condition results from an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour, triggered by hormonal shifts, sun exposure, or even certain medications.
Key features:
- Brown or grey patches are typically found on the cheeks, forehead, and chin.
- Common in pregnant women or individuals on hormonal therapy or contraceptives.
- Aggravated by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure.
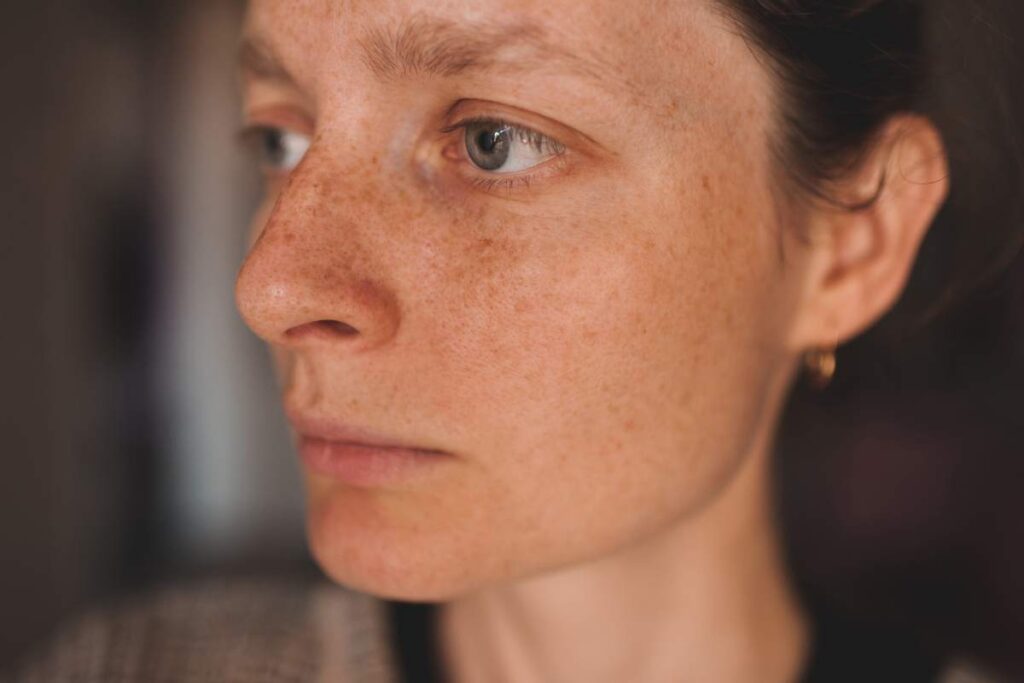

Freckles
Freckles are small, flat, circular spots that are usually lighter than melasma. They often develop in childhood and are more prominent in people with fair skin or those who have spent considerable time in the sun. Unlike melasma, freckles are not caused by hormonal changes but by the skin’s response to UV radiation. The amount of melanin produced in the skin increases in response to sunlight, causing small, concentrated pigment spots.
Key features:
- Small, light brown spots, often appear on sun-exposed areas like the face, shoulders, and arms.
- More common in people with light or fair skin.
- Increase in number and darkness with sun exposure, often fading in the winter.
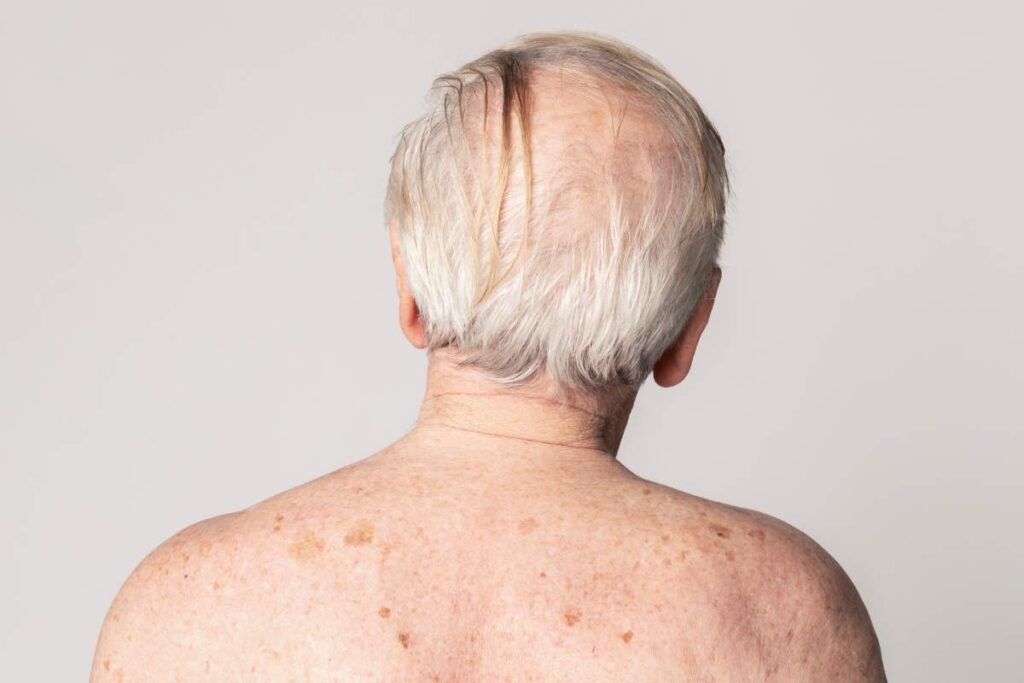
Age Spots (Solar Lentigines)
Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are flat, brown, or black spots that usually appear in areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun. They typically develop after the age of 40 but can appear earlier in people who have had significant sun exposure over their lifetime. Age spots are caused by a combination of UV exposure and the natural ageing process, where melanin builds up in certain areas of the skin.
Key features:
- Larger, flat spots, often darker than freckles.
- Typically appear on the face, hands, shoulders, and arms — areas most exposed to sunlight.
- Common in older adults but can occur earlier with significant sun damage.
Can Melasma, Freckles, and Age Spots Be Removed?
The short answer is yes — but with varying degrees of difficulty and long-term effectiveness. Let’s explore the available treatment options.
1. Topical Treatments
One of the first approaches to treating hyperpigmentation like melasma, freckles, and age spots is through topical creams and lotions. These products often contain ingredients that lighten the skin or reduce melanin production.
- Hydroquinone: Often considered the gold standard for lightening hyperpigmentation, hydroquinone decreases the amount of melanin in the skin. Available in over-the-counter and prescription strengths, it can be effective for melasma and age spots, though less so for freckles.
- Retinoids: Derived from Vitamin A, retinoids help by promoting skin cell turnover and fading dark spots over time. They can also prevent new spots from forming, making them a good long-term solution for preventing future hyperpigmentation.
- Vitamin C: As a powerful antioxidant, Vitamin C can brighten the skin and reduce the appearance of dark spots. It is commonly found in serums and creams and can be effective for mild pigmentation issues.
- Azelaic Acid: Known for its anti-inflammatory and brightening properties, azelaic acid is another option for treating melasma and age spots, though results may take several months to become noticeable.
- Kojic Acid and Liquorice Extract: Natural skin-lightening ingredients like kojic acid and liquorice extract can inhibit melanin production, leading to a gradual reduction in dark spots.
While topical treatments can be effective, they often require patience and persistence, as results can take weeks or months to become apparent. They are generally more effective for milder cases of hyperpigmentation and may not be sufficient for deeper pigmentation issues.
2. Chemical Peels
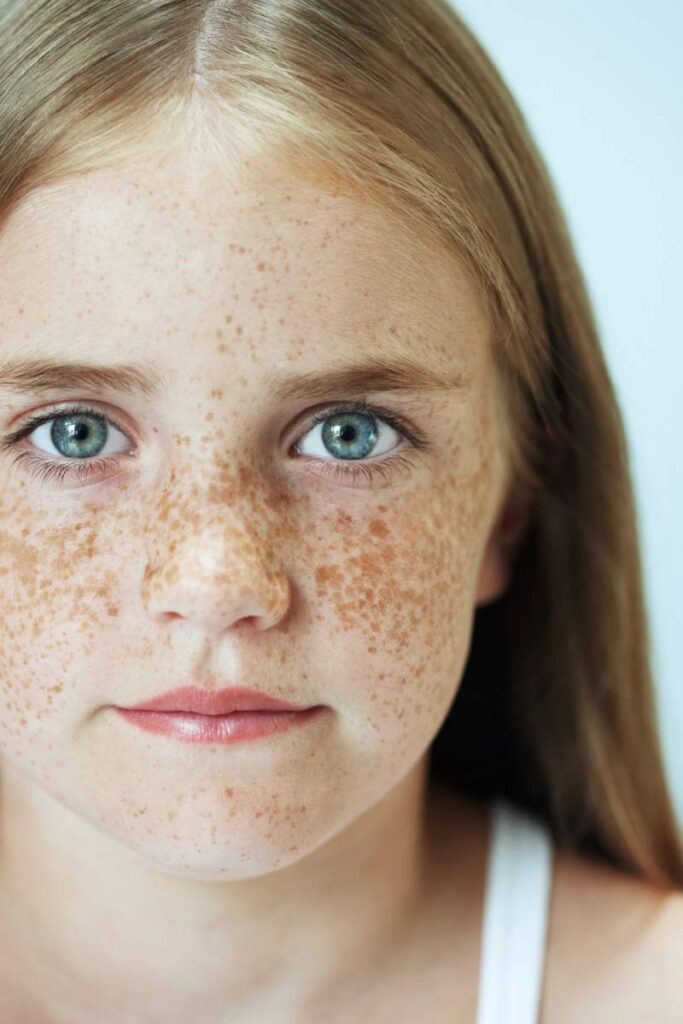

Chemical peels involve applying an acid solution to the skin to remove its outer layers. This can help fade dark spots, revealing fresher, more even-toned skin beneath.
- Glycolic Acid Peels: One of the most popular types of chemical peels, glycolic acid helps exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of pigmentation.
- TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid) Peels: TCA peels are more potent than glycolic peels and can target deeper pigmentation like melasma and age spots. However, they require longer recovery times and come with a higher risk of side effects, including scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Chemical peels can be highly effective, particularly for age spots and melasma, but they carry some risks and require proper aftercare to avoid complications like infections or additional pigmentation issues.
3. Laser Treatments
Lasers are a powerful and increasingly popular method for treating hyperpigmentation. They work by targeting melanin directly, breaking up the pigment so that the body can naturally eliminate it.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): IPL treatments use broad-spectrum light to target melanin in the skin, making them effective for age spots and melasma. However, IPL is not always suitable for darker skin tones as it may cause further pigmentation problems.
- Fractional Laser Resurfacing: This treatment targets both the surface and deeper layers of the skin to stimulate new collagen production and fade pigmentation. It can be effective for deeper melasma and age spots, but multiple sessions are usually required for the best results.
Laser treatments are generally considered safe, though they may cause temporary side effects like redness, swelling, and peeling. The cost of laser treatment can be high, and it often takes multiple sessions to see significant improvement.
4. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing dark spots with liquid nitrogen, causing the skin to blister and peel off, revealing new skin beneath. This method is particularly effective for age spots but is less commonly used for freckles or melasma.
Cryotherapy is a quick procedure and generally has minimal recovery time, though there is a slight risk of scarring or hypopigmentation (lightening of the skin) after treatment.
5. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive treatment that uses tiny crystals or a diamond tip to exfoliate the top layer of the skin. It is a gentler option compared to chemical peels and lasers but can still help fade superficial pigmentation issues like freckles and mild age spots.
Because it works on the surface of the skin, microdermabrasion is less effective for deep melasma but can improve overall skin tone and texture.
Preventing Recurrence
While many treatments can fade or remove melasma, freckles, and age spots, preventing their recurrence is equally important. Sun protection is essential in managing these conditions, as UV exposure can trigger or worsen hyperpigmentation.
- Daily Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and reapply it every two hours when outside. Sunscreen is crucial even on cloudy days or during winter months, as UV rays can penetrate through clouds.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing can shield your skin from UV damage.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit UV radiation that can exacerbate hyperpigmentation and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Final Thought
Melasma, freckles, and age spots are common forms of hyperpigmentation that can be distressing for those who experience them. While removal is possible, the effectiveness of treatments varies depending on the type and depth of pigmentation.
Options range from topical treatments to laser therapy, with each offering varying degrees of success. It’s essential to work with a dermatologist to determine the best course of action and to prioritize sun protection to prevent future spots from forming.
For those seeking professional cosmetic treatments, Kamol Cosmetic Hospital, one of the world’s leading cosmetic surgery hospitals, offers advanced procedures for hyperpigmentation and other skin concerns, ensuring safe and effective results.
4